Ancient Greek Studies
PROGRAM OVERVIEW
Ancient Greek Studies is based on an interdisciplinary approach to studying Ancient or Classical Greek within the larger socio-economic, cultural, and political realm of the ancient world.
The Ancient Greek Studies program aims at providing introductory, functional, and mastery-grade language acquisition and proficiency through gradually comprehensive instruction. The program is ideal for students and teachers of Classical Studies who are interested in comprehending Ancient Greek within an authentic communicative learning environment.
Source texts include the works of Aristotle, Plato, Homer, and Xenophon.
Courses within the Ancient Greek Studies program are taught through an interdisciplinary approach that enables the learner to acquire Ancient Greek but also to understand the wider socio-economic, cultural, and political realms of the ancient world.
During each course, at a progressively increasing level of fluency development that is achieved through structured practice and extensive drills, students build the language acquisition skills required to read, write, listen, understand, and speak Ancient Greek as it is spoken by native Greek speakers.
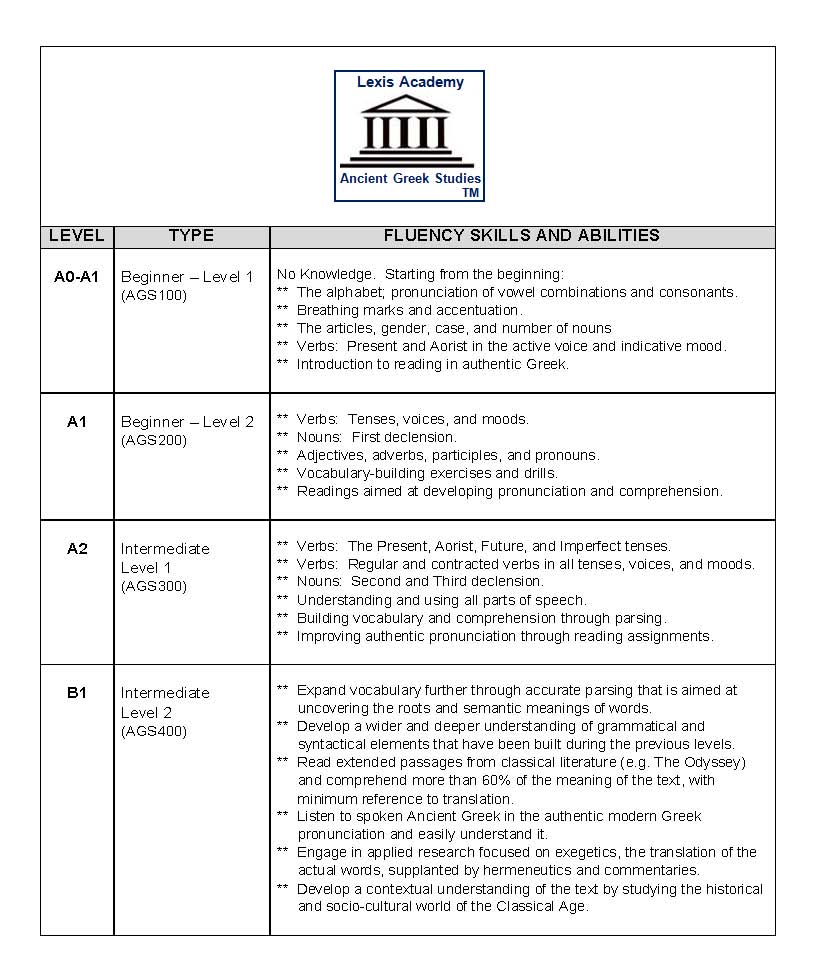
Based on personal needs and the outcomes of placement tests, adult Greek Language Learners have the opportunity to enroll in the following beginner and intermediate courses that are designed to take the learner from the very basic vocabulary to complete mastery of Ancient Greek:
AGS100: Ancient Greek Beginner Level 1 (A1)
AGS200: Ancient Greek Beginner Level 2 (A1)
AGS300: Ancient Greek Intermediate Level 1 (A2)
AGS400: Ancient Greek Intermediate Level 2 (B1)
Most students typically enter the program by starting at the Beginner level.
Example topics of instruction and learning objectives at the Beginner level include:
• Reading and writing the alphabet in authentic Greek.
• Understanding and using accents and breathing marks.
• Building vocabulary through reading, speaking, listening and translation drills.
• Writing correct sentences according to emphatic subject, verb, or object needs.
• Listening and pronouncing authentically the phonemic system of Ancient Greek.
• Listening and pronouncing Ancient Greek in authentic and current native speech.
• Building helpful vocabulary through reading, speaking, listening and translation drills.
• Reading and deconstructing the vocabulary, grammar, and syntax of designated passages.
• Understanding and using nouns, adjectives, participles, verbs, and all other parts of speech.
• Developing competent use of cases, numbers, and genders for all declinable parts of speech.
COURSE OBJECTIVES AND LEARNING OUTCOMES
Course objectives and learning outcomes at each level follow are summarized below.
These proficiency development targets are based on the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR or CEF) that defines teaching, learning, and assessment processes in Second Language Acquisition.
Democracy – The Olympics
Greece (Hellas) is the birthplace of democracy, a vote-based system of government that remains in practice in most of the world today. It is also the land where the Olympic Games were invented and held in honor of Zeus, the very first event was held in 776 BC. All conflicts were ceased before and during the event to enable spectators to travel and attend the games.
Politics
Politics was of utmost importance in Ancient Greece. Every citizen had the right, and the obligation, to voice their opinion publicly without fear of reprisal or rebuke. A citizen who chose not to participate in public affairs was considered selfish and was called a private citizen, “ιδιώτης”, and this word in English became “idiot”.
Foundations of Western Culture
During the 5th and 4th centuries, Greek civilization had reached its highest point as an economic and socio-cultural power in the ancient world. Even though Greek democracy was short-lived, its focus on philosophy, language, politics, and the sciences deeply influenced the Roman Empire. As the Roman expansion spread, it diffused Greek knowledge and planted the seeds for the subsequent development of Western culture as it is known today.
Visiting Athens to Learn About Ancient Greece
When you are in Athens, you can buy a combined ticket, valid for five days from the day of purchase. The combined ticket allows you to visit all the ticketed archaeological sites in central Athens and it costs 30 Euros.
The Athens combined ticket for archaeological sites includes entrance to:
** The Acropolis of Athens
** The Ancient Agora of Athens and the Museum of the Ancient
Agora
** Kerameikos and the Archaeological Museum of Kerameikos
** The Temple of Olympian Zeus (Olympieio)
** The Roman Agora of Athens and the Tower of the Winds
** Hadrian’s Library
** Aristotle’s Lyceum (Archaeological site of Lykeion)
Source: https://realgreekexperiences.com/
Notes from the Living History of Greece
Ancient Greek civilization, the period following Mycenaean civilization that ended about 1200 BCE, to the death of Alexander the Great, in 323 BCE. It was a period of political, philosophical, artistic, and scientific achievements that formed a legacy with unparalleled influence on Western civilization.
The ancient Greek alphabet was the first true alphabet, because it was the first writing system in which every letter represents a specific sound that had letters representing vowels. The Greek alphabet was based on the earlier Phoenician abjad, which is only had consonants. The Greeks repurposed Phoenician letters representing consonant sounds that did not exist in their language as vowels. The Latin alphabet, which is the alphabet used today to write the English language is derived from the Etruscan alphabet, which is, in turn, derived from the Greek alphabet.
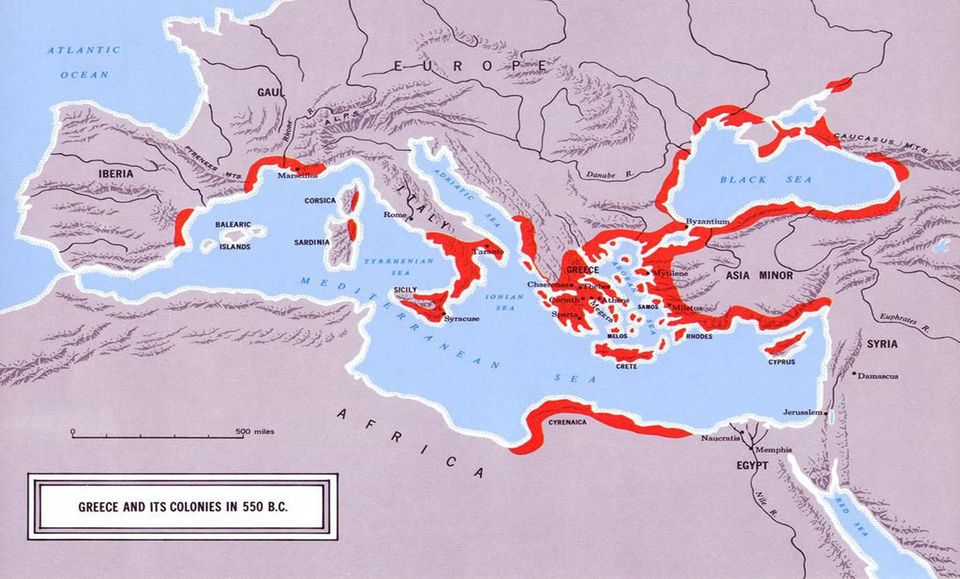
Spread across the Mediterranean Sea in more than a thousand small city-states, Ancient Greeks drove, promoted and enabled the free flow of trade, people, ideas, while also peacefully building Magna Graecia communities in Europe, Africa, the Middle East, and Asia. The secret of the Ancient Greeks’ greatness lay in their extraordinary ambition and competitiveness that has influenced modern society in at least ten fields of human endeavor:
01] Philosophy
02] Mathematics
03] Education
04] Literature
05] Sports
06] Medicine
07] Science
08] Politics
09] Architecture
10] Warfare
Sources: Encyclopedia Britannica; https://www.historyanswers.co.uk;